Disa 2
Project Info
Client
Disa
Total Land Area
1000 m2
Floors
5 floors & 2 common spaces
Project Infrastructure Area
4131 m2
Location
No14, Kabkanian st, Keshavarz blvrd, Tehran, Iran.
Project Time Line
July 2014 -September 2016
The design idea
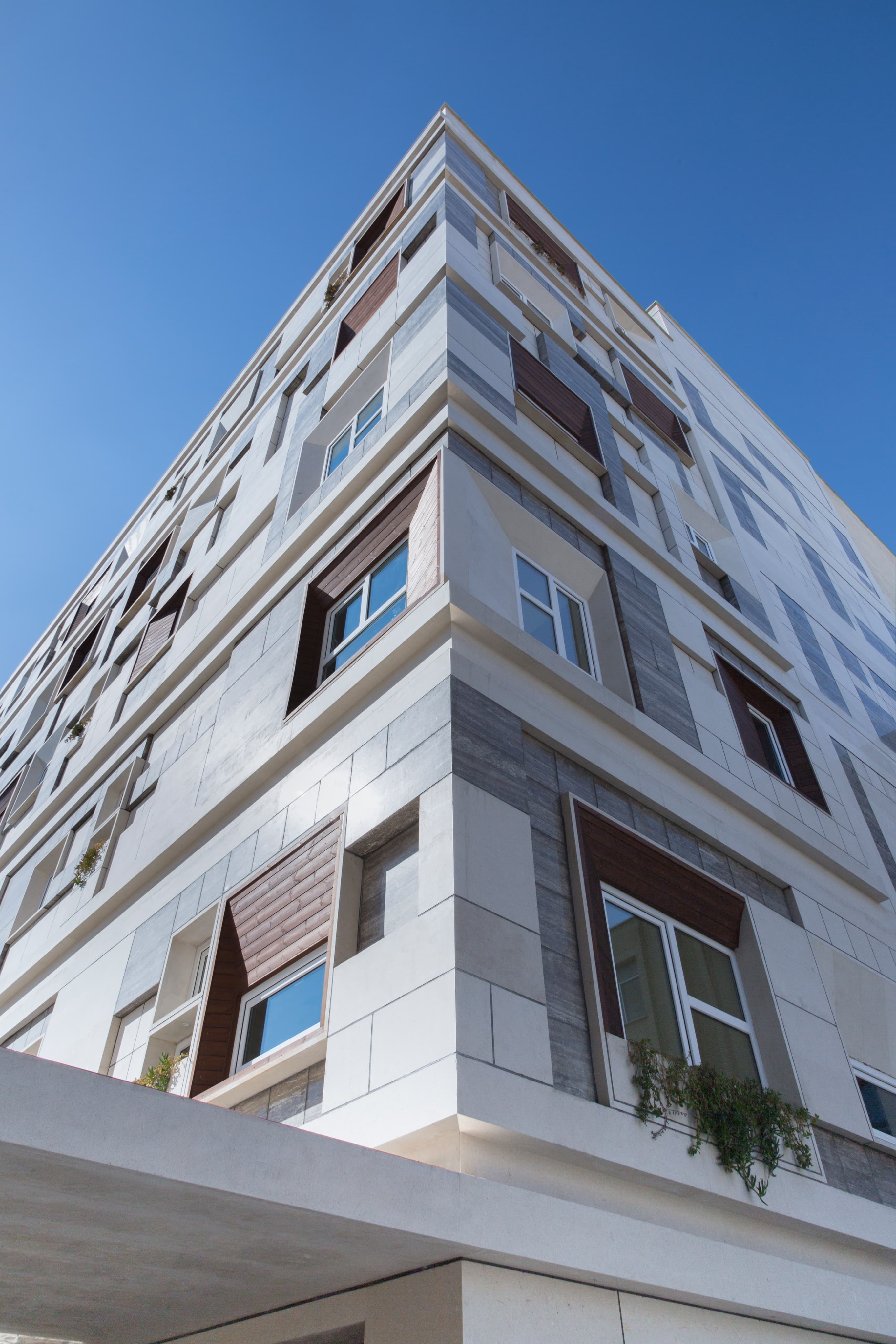
In Iranian traditional architecture, enclosed balconies with controlled views are principle. Senasir, in southern Iran, is one of the greatest examples of these covered and private balconies
A proper balcony design was critical given the project's enormous breadth of land. As a result, the main architectural idea centered on contemporary balconies as dangling protrusions, but also incorporating Senasirs' vintage atmosphere

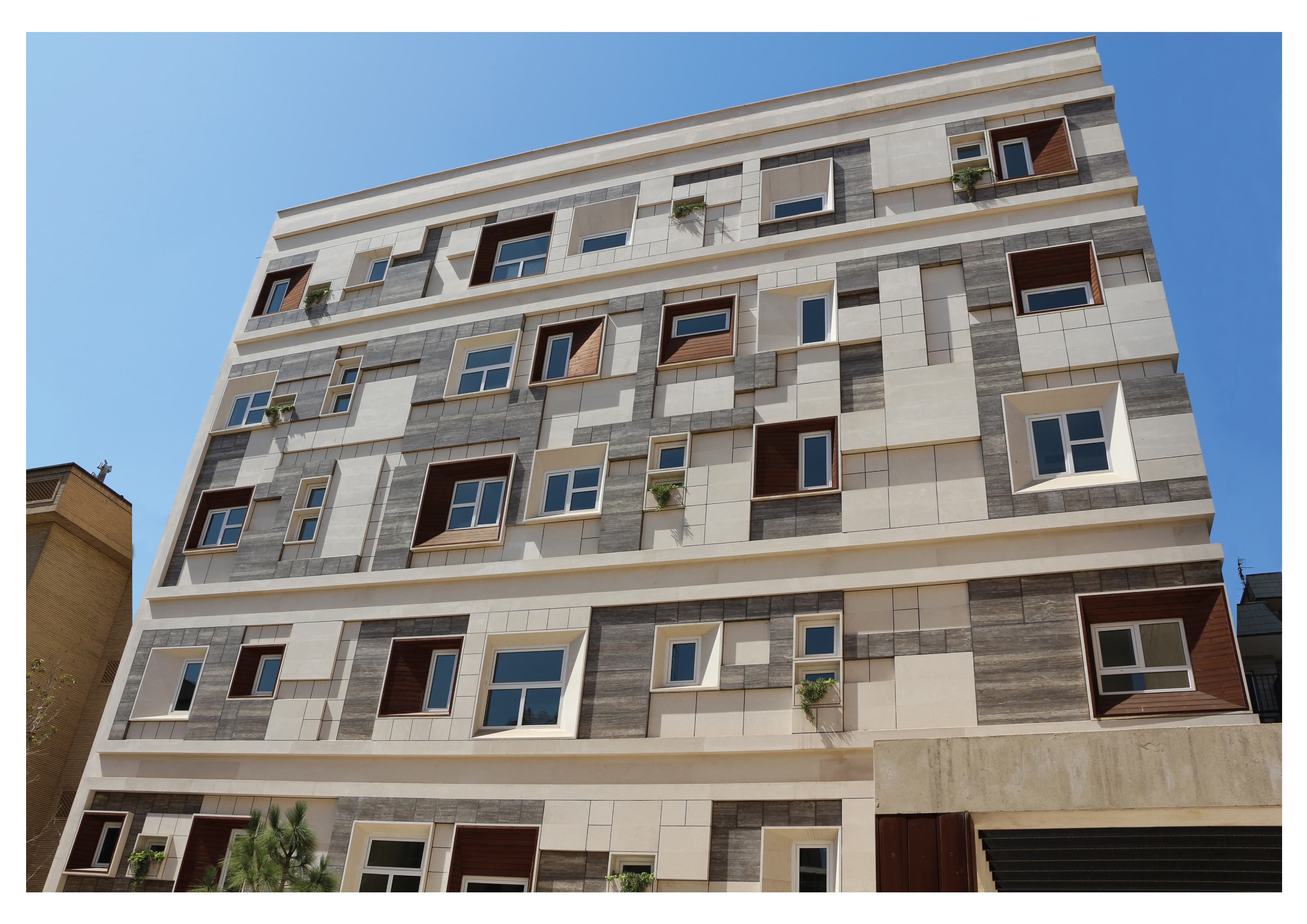
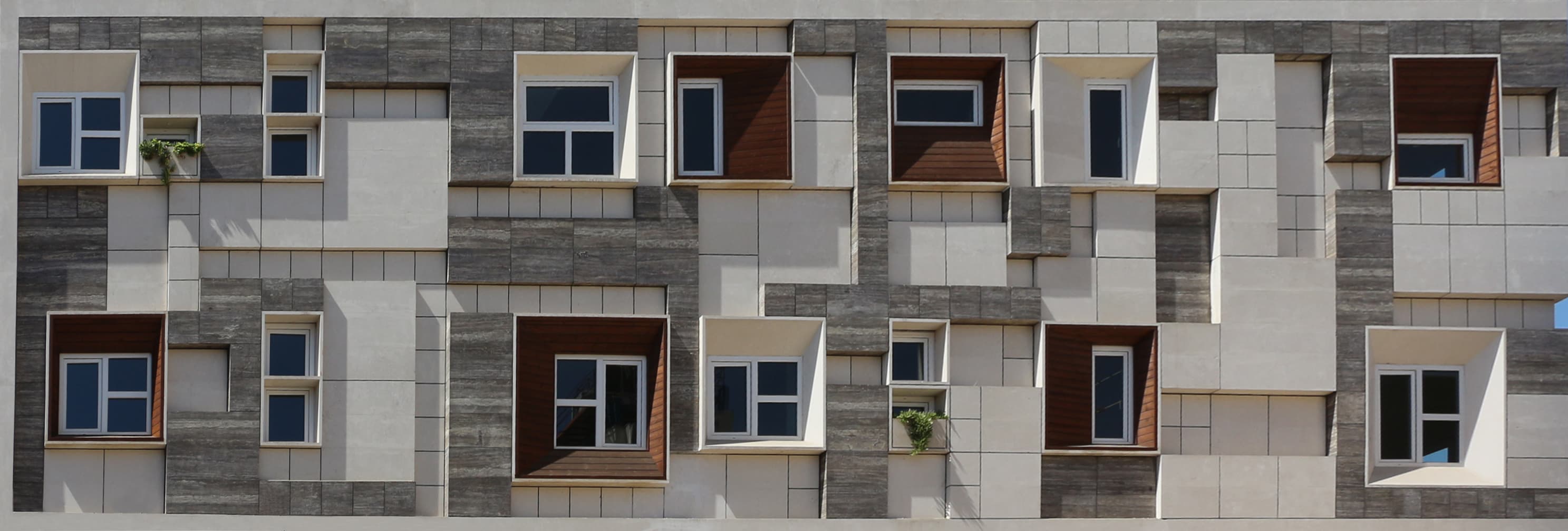
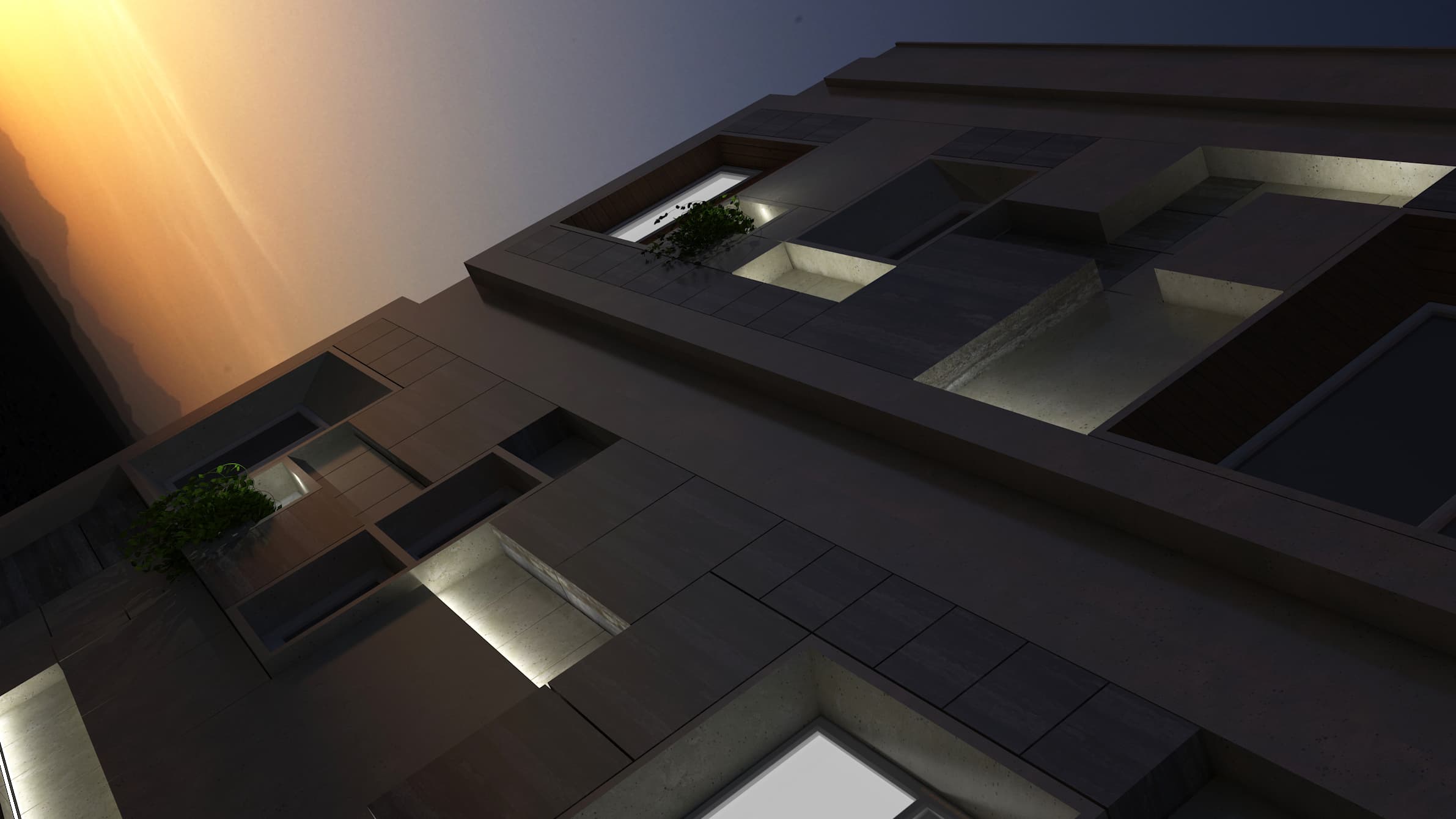
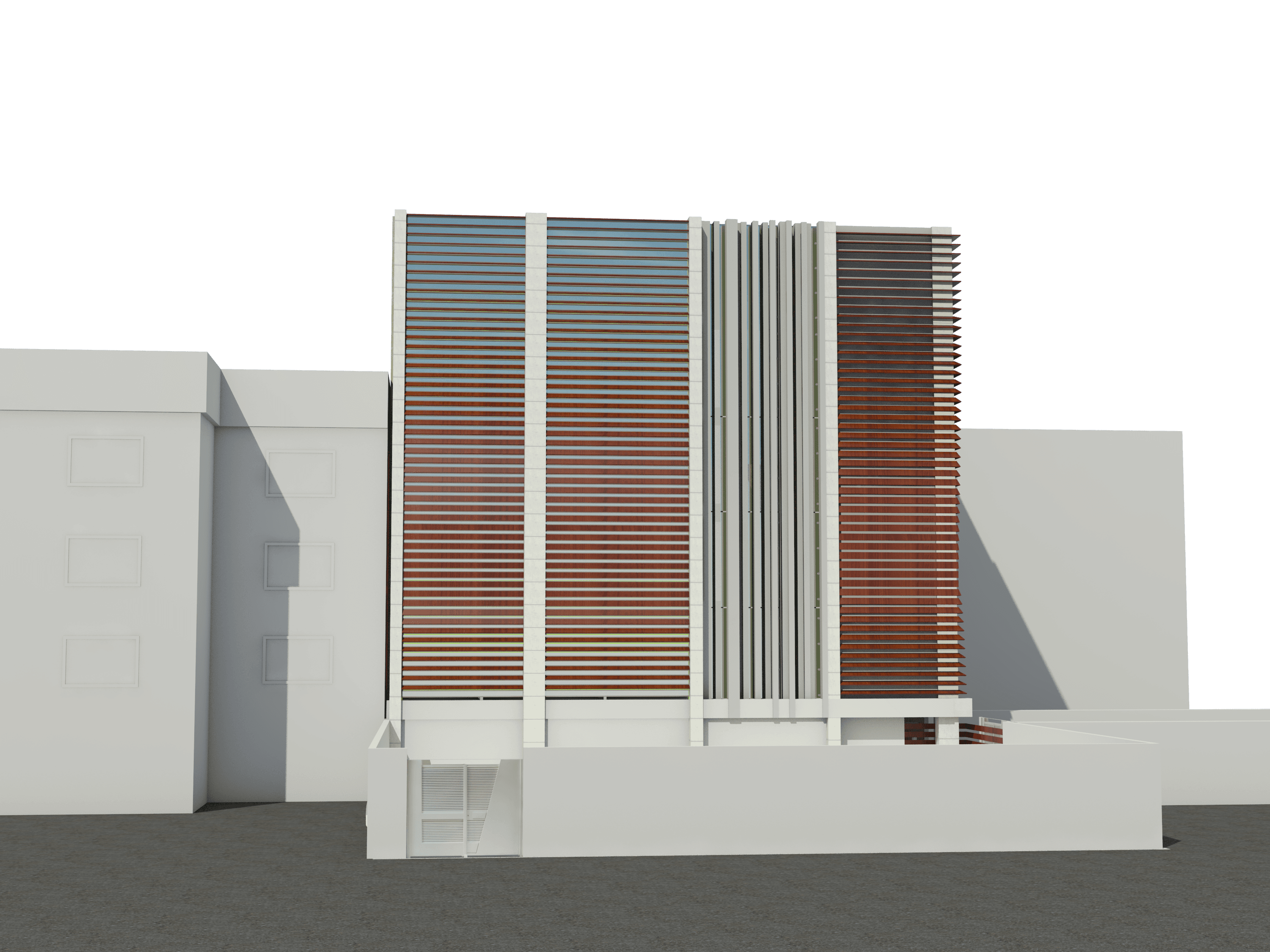
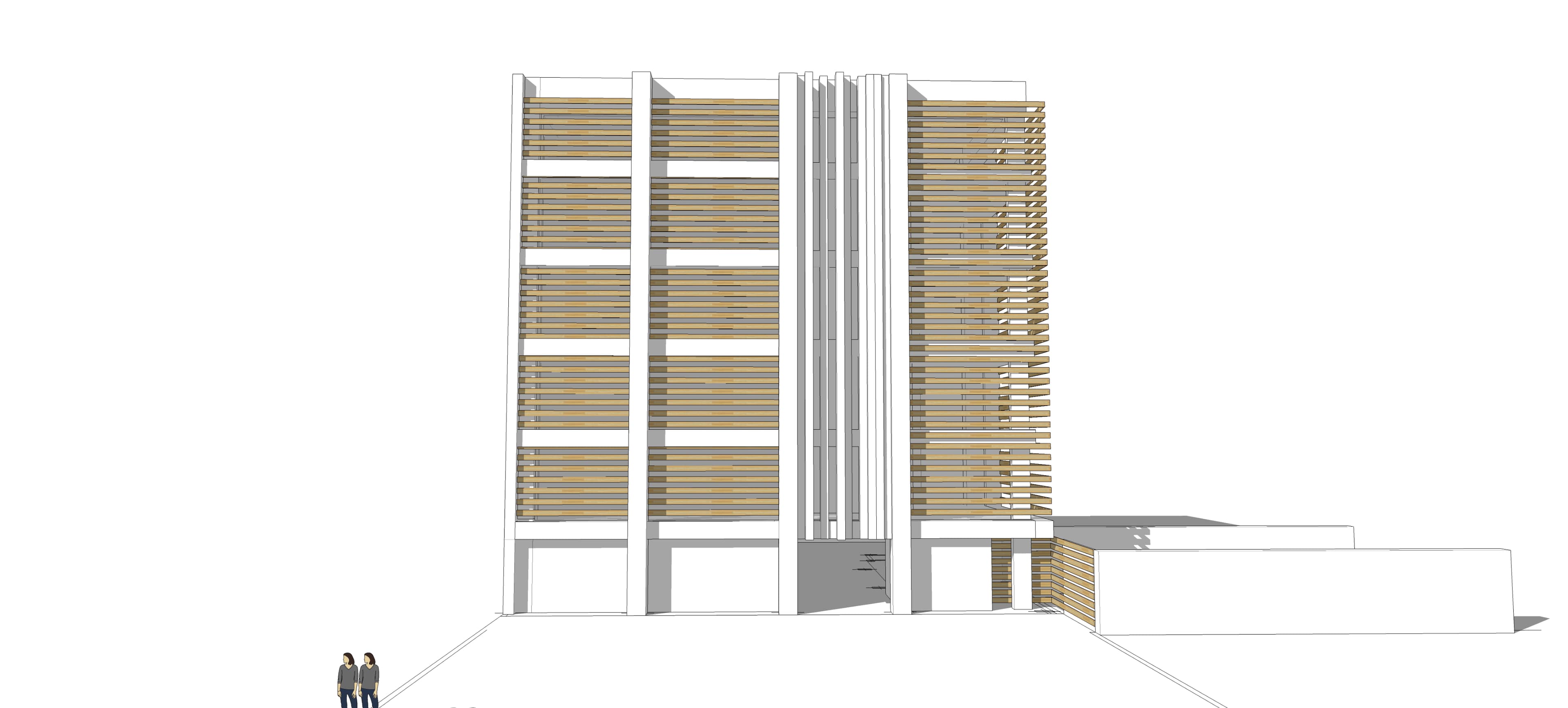
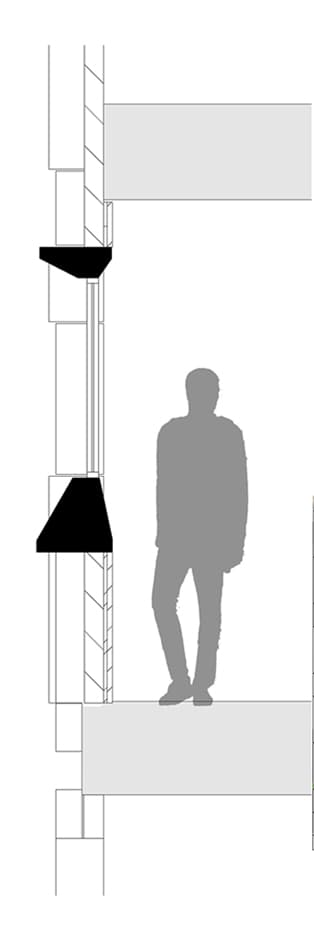
To manage glare and heat from the sun, we employed vertical and horizontal shaders at the start of the design phase, but subsequently we used a 40 x 40 module unit system both in plan and on the façade.
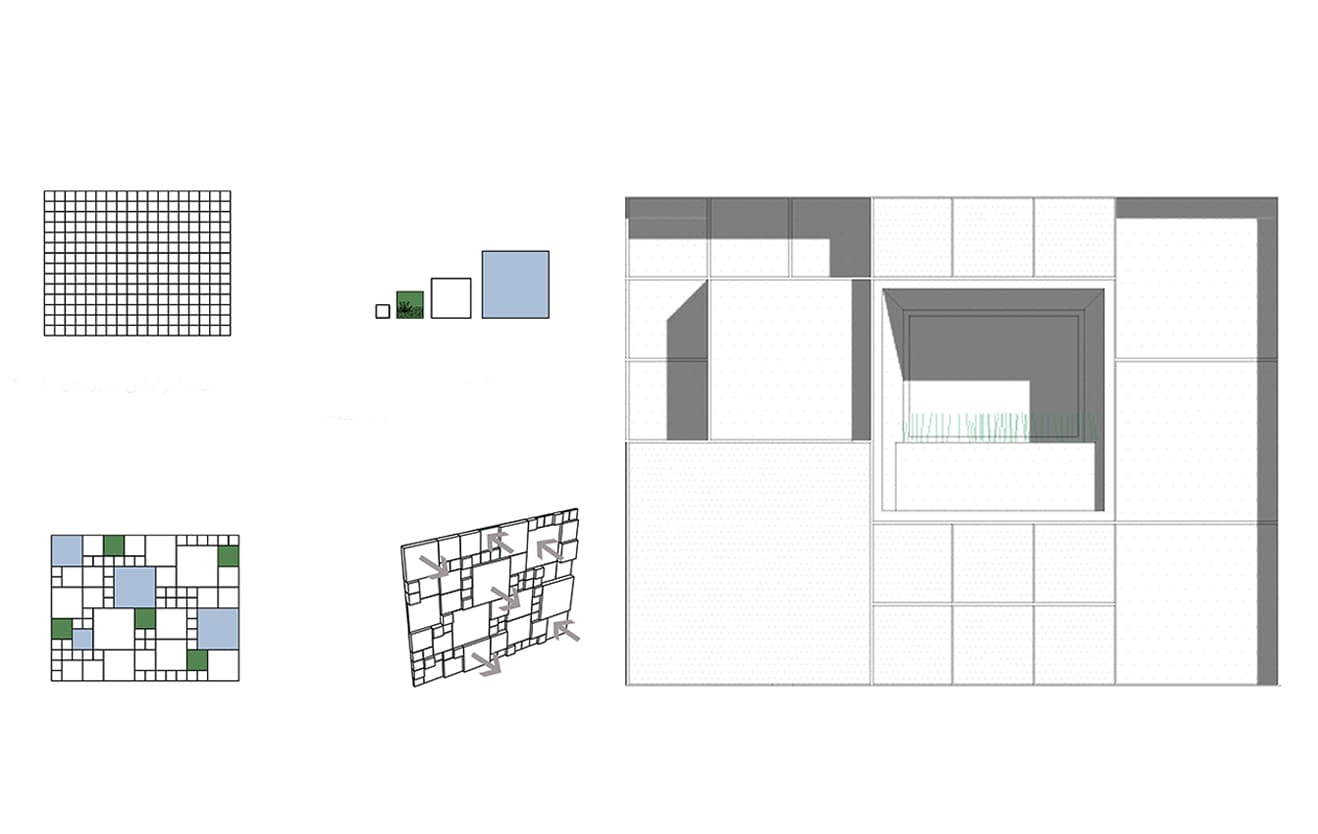
It was designed by arranging them in patterns of 40*40, 80*80, 120*120, and 160*160 modules on a 40*40 grid. Despite its complexity, these statistics are driven by stone scoop, which is the primary material used in pavements and façades, resulting in less waste and lower costs for the client.
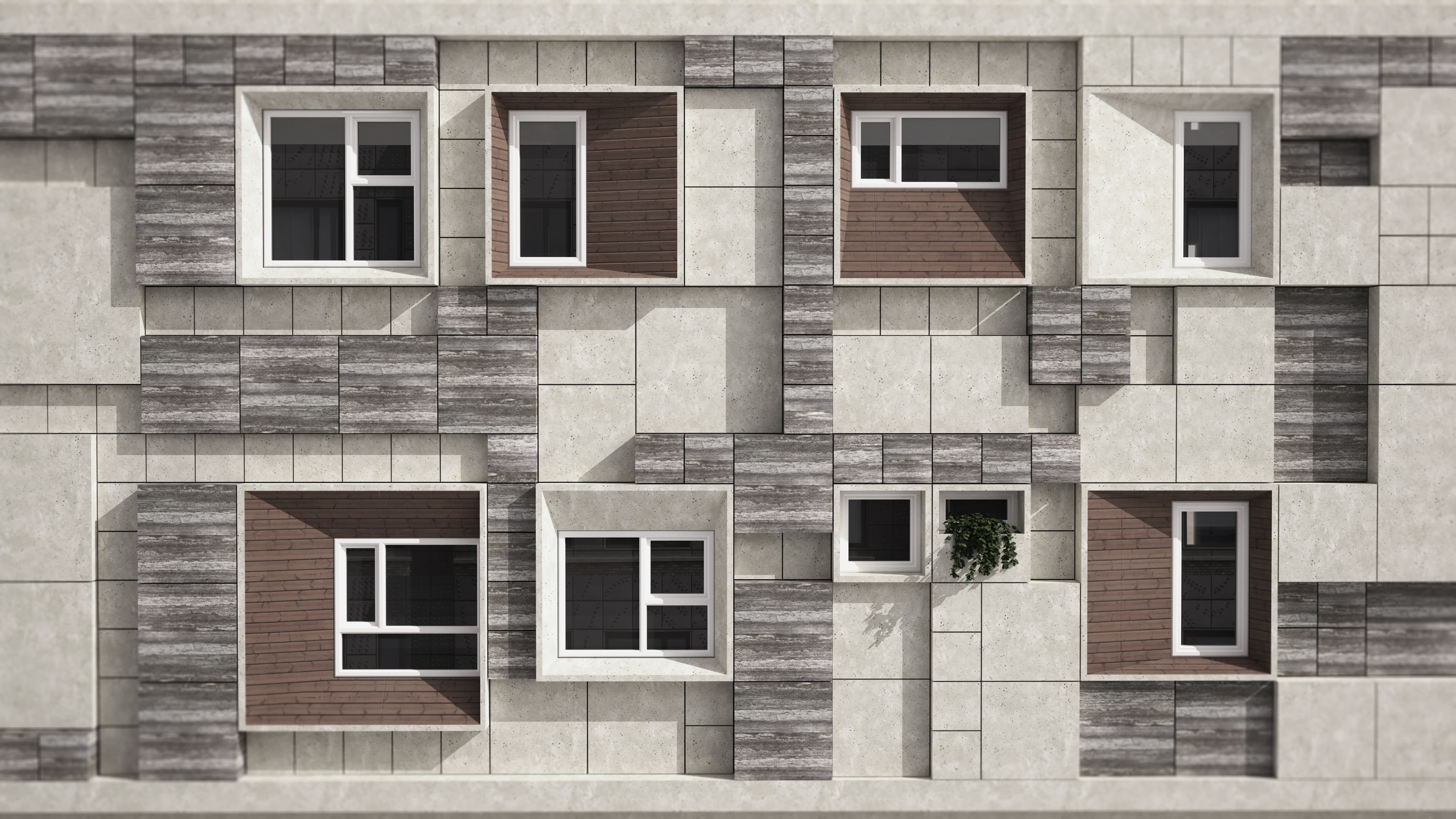
The building's exterior and layout are structured around a 40x40 module unit system, applied both in the floor plan and on the façade. This modular system is composed of various sized units (40x40, 80x80, 120x120, and 160x160) arranged on a 40x40 grid, allowing for a balance of simplicity and dynamic design.
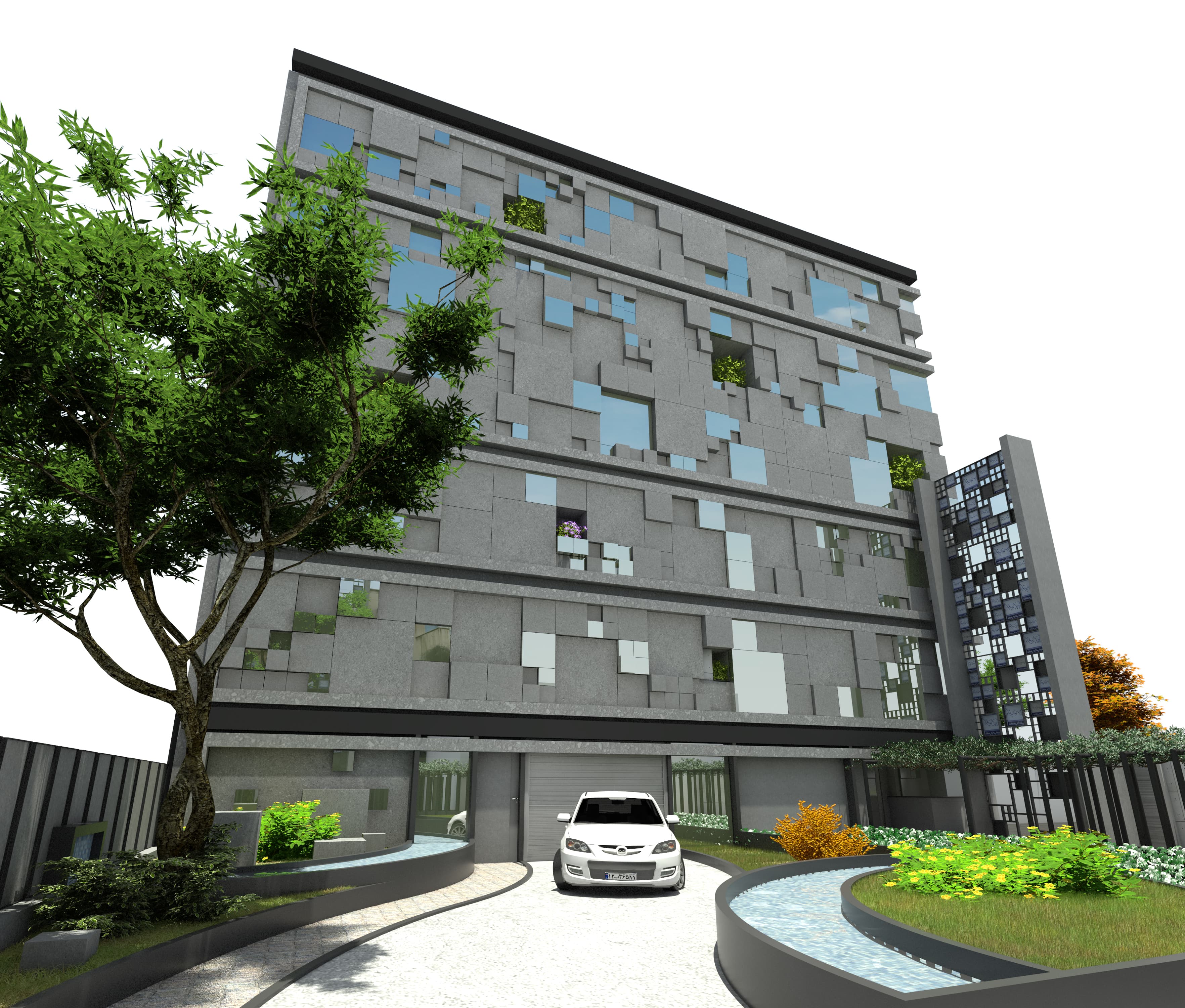

Despite the apparent complexity of these modular patterns, the underlying approach is driven by the use of stone scoop—a durable, natural material predominantly utilized in both the pavements and the façade. This method allowed the architects to reduce material waste significantly while cutting costs for the client. The precise calculations and modular planning made the construction more efficient, as each unit was designed to fit seamlessly with the others, maintaining harmony across the entire building.
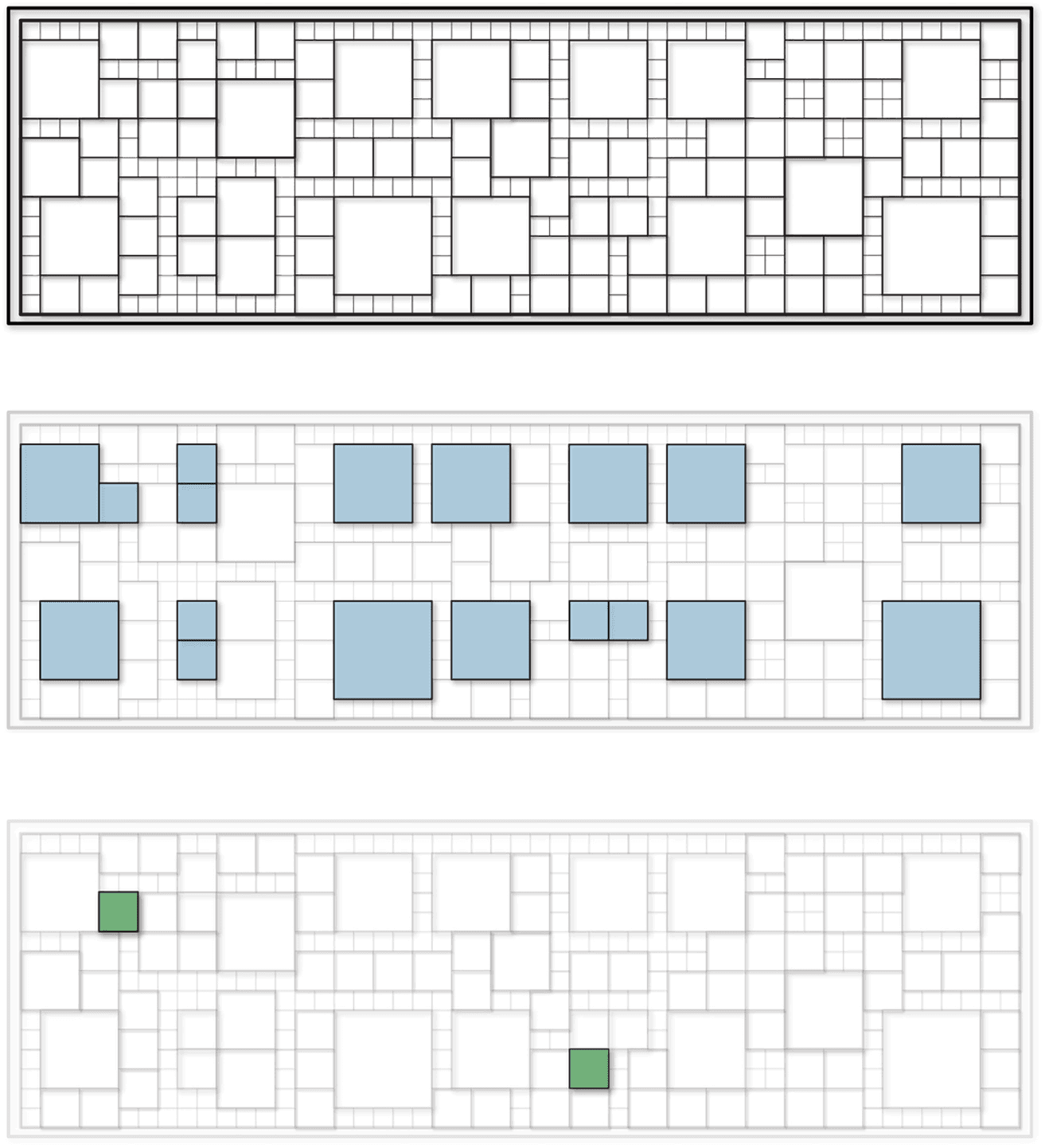
The building's exterior and layout are structured around a 40x40 module unit system, applied both in the floor plan and on the façade. This modular system is composed of various sized units (40x40, 80x80, 120x120, and 160x160) arranged on a 40x40 grid, allowing for a balance of simplicity and dynamic design.
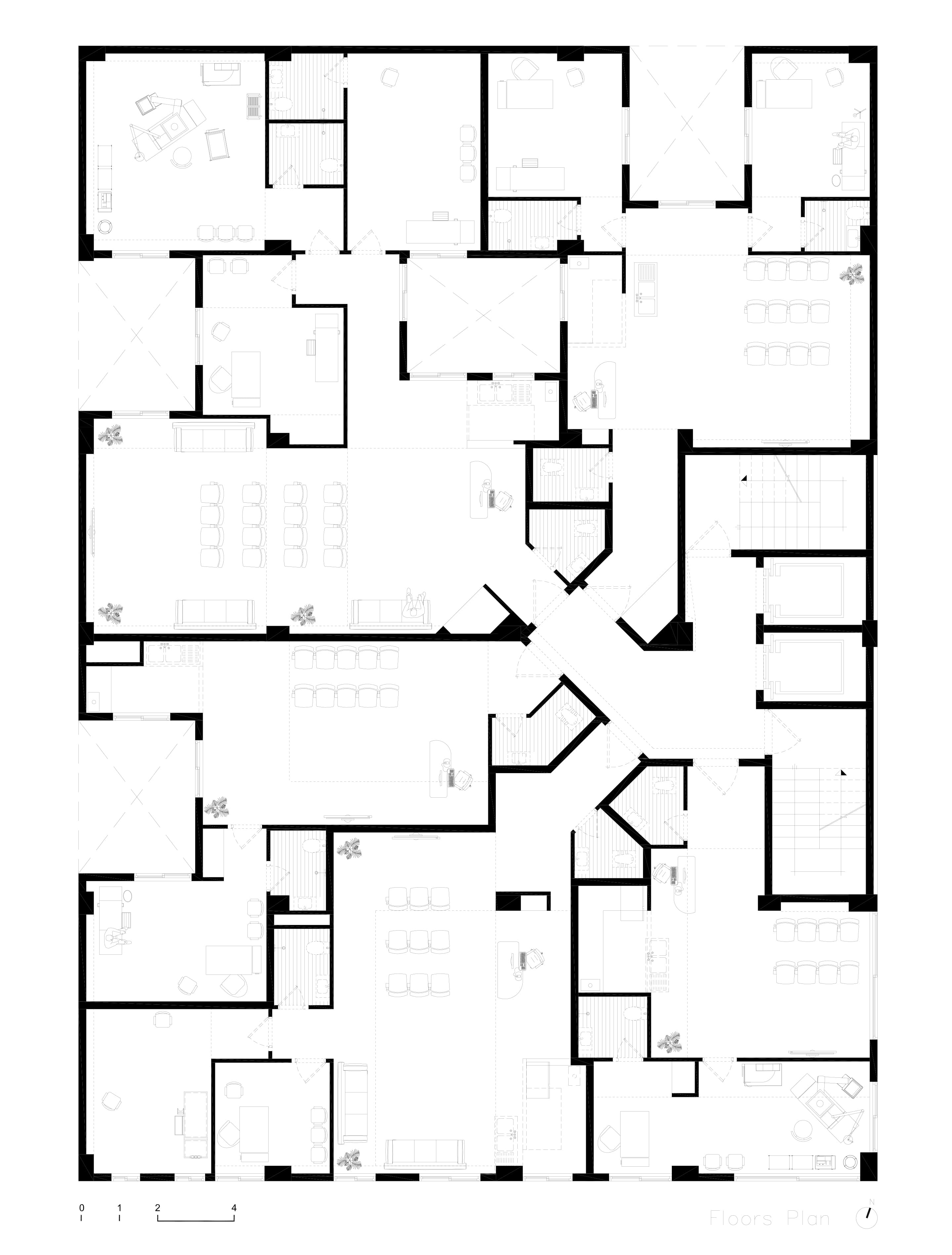
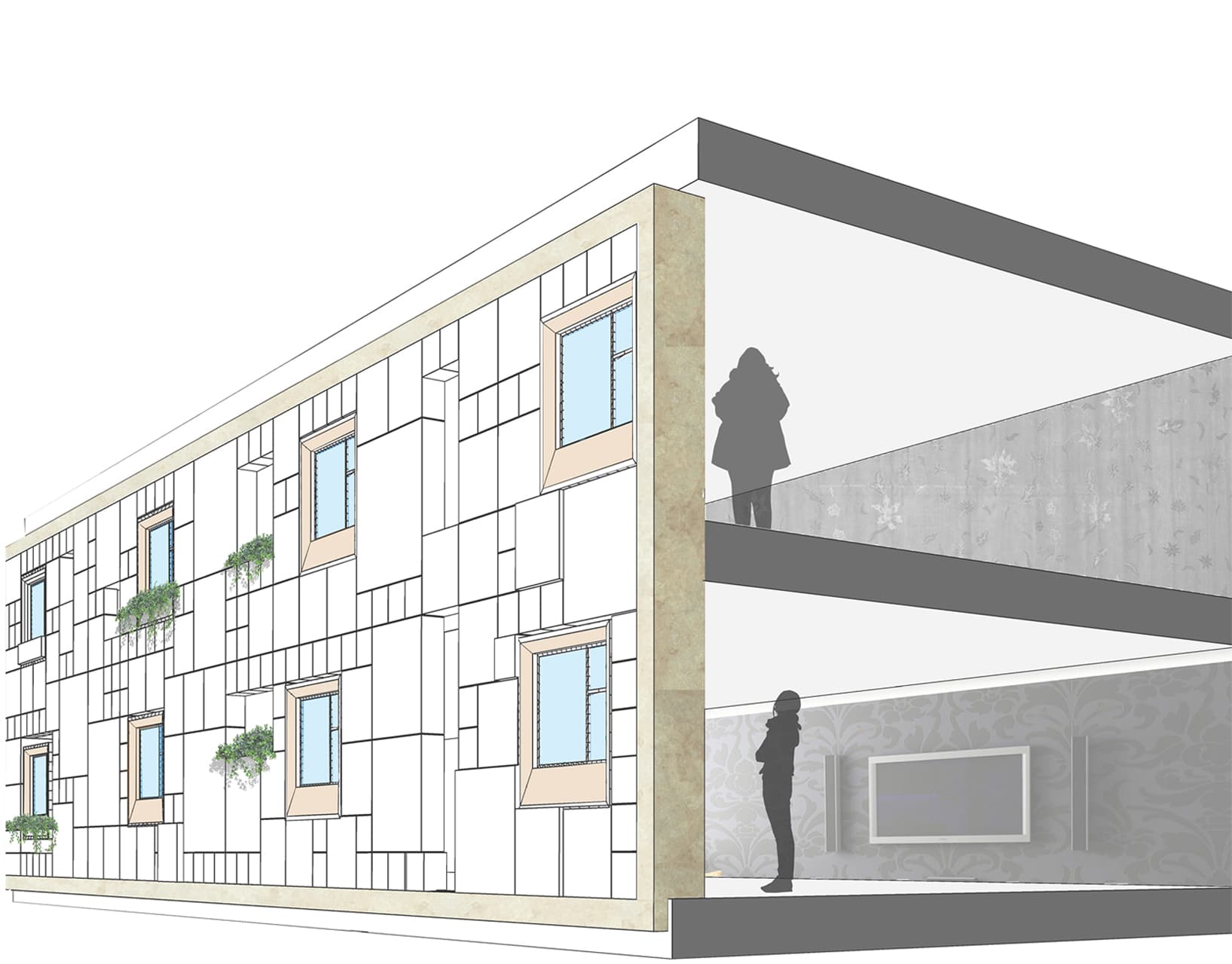
In addition to its technical innovations, the building's infrastructure was carefully designed to accommodate its medical function. The structure includes five floors dedicated to clinical and medical services, along with two common spaces designed for patient and staff interaction, ensuring a fluid and efficient workflow. The thoughtful integration of the shading system and modular layout makes the building not just a functional space, but also an environmentally conscious one, reducing energy consumption and enhancing the overall user experience.
In addition to its technical innovations, the building's infrastructure was carefully designed to accommodate its medical function. The structure includes five floors dedicated to clinical and medical services, along with two common spaces designed for patient and staff interaction, ensuring a fluid and efficient workflow. The thoughtful integration of the shading system and modular layout makes the building not just a functional space, but also an environmentally conscious one, reducing energy consumption and enhancing the overall user experience.
Despite the apparent complexity of these modular patterns, the underlying approach is driven by the use of stone scoop—a durable, natural material predominantly utilized in both the pavements and the façade. This method allowed the architects to reduce material waste significantly while cutting costs for the client. The precise calculations and modular planning made the construction more efficient, as each unit was designed to fit seamlessly with the others, maintaining harmony across the entire building
In addition to its technical innovations, the building's infrastructure was carefully designed to accommodate its medical function. The structure includes five floors dedicated to clinical and medical services, along with two common spaces designed for patient and staff interaction, ensuring a fluid and efficient workflow. The thoughtful integration of the shading system and modular layout makes the building not just a functional space, but also an environmentally conscious one, reducing energy consumption and enhancing the overall user experience.
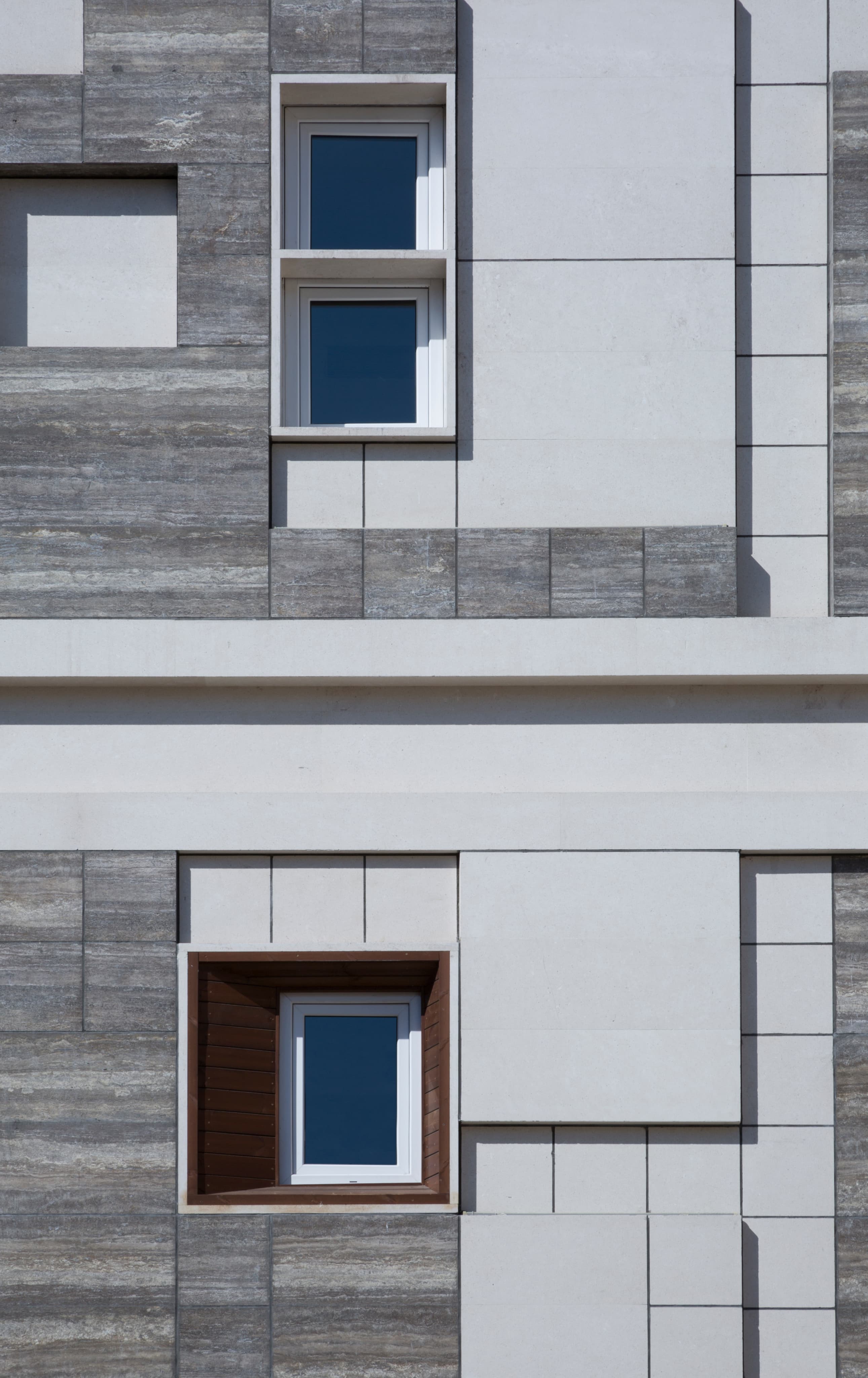

In addition to its technical innovations, the building's infrastructure was carefully designed to accommodate its medical function. The structure includes five floors dedicated to clinical and medical services, along with two common spaces designed for patient and staff interaction, ensuring a fluid and efficient workflow. The thoughtful integration of the shading system and modular layout makes the building not just a functional space, but also an environmentally conscious one, reducing energy consumption and enhancing the overall user experience.

In addition to its technical innovations, the building's infrastructure was carefully designed to accommodate its medical function. The structure includes five floors dedicated to clinical and medical services, along with two common spaces designed for patient and staff interaction, ensuring a fluid and efficient workflow. The thoughtful integration of the shading system and modular layout makes the building not just a functional space, but also an environmentally conscious one, reducing energy consumption and enhancing the overall user experience.
Other Images




